INDICATIONS AND USES
Allergy and anaphylaxis: Bronchial asthma, drug hypersensitivity reactions, serum sickness, angioneurotic oedema, anaphylaxis.
Respiratory disease: Allergic pneumonitis, asthma, occupational asthma, pulmonary aspergillo¬ sis, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary alveolitis, aspiration of foreign body, aspiration of stomach contents, pulmonary sarcoid, drug induced lung disease, adult respiratory distress syndrome, spasmodic croup.
Rheumatic disorders: Rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, juvenile chronic arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, mixed connective tissue disease. Arteritis/collagenosis: Giant cell arteritis/polymyalgia rheumatica, mixed connective tissue disease, polyarteritis nodosa, polymyositis.
Blood disorders: Haemolytic anaemia (autoimmune), leukaemia (acute and lymphocytic), lymphoma, multiple myeloma, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Cardiovascular disorders: Post myocardial infarction syndrome, rheumatic fever with severe carditis.
Endocrine disorders: Primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency, congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Gastro-intestinal disorders: Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, persistent celiac syndrome, autoimmune chronic active hepatitis, multisystem disease affecting liver, biliary peritonitis. Infections: Military tuberculosis, mumps orchitis (adult), tuberculous meningitis, rickettsial disease.
Muscular disorders: Polymyositis, dermatomyositis.
Neurological disorders: Infantile spasms, ShyDrager syndrome, sub-acute demyelinating polyneuropathy.
Ocular disease: Scleritis, posterior uveitis, retinal vasculitis, pseudo tumours of the orbit, malignant ophthalmic Graves disease.
Renal disorders: Lupus nephritis, acute intersititial nephritis, minimal change glomerulonephritis. Skin disorders: Pemphigus vulgaris, bullous pemphigoid, systemic lupus erythematosus, pyoderma gangrenosum.
Miscellaneous: Sarcoidosis, hyperpyrexia, Behcets disease, immunosuppression in organ transplantation.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The initial dosage of Kidpred may vary from 5 mg to 60 mg daily depending on the disorder being treated. Divided daily dosage is usually used.
The appropriate individual dose must be determined by trial and error and must be re-evaluated regularly according to activity of the disease.
In general, initial dosage shall be maintained or adjusted until the anticipated response is observed. The dose should be gradually reduced until the lowest dose, which will maintain an adequate clinical response is reached.
During prolonged therapy, dosage may need to be temporarily increased during periods of stress or during exacerbations of the disease. When the drug is to be stopped, it must be withdrawn gradually and not abruptly.
Intermittent dosage regimen: A single dose of Kidpred in the morning on alternate days or at longer intervals is acceptable therapy for some patients. When this regimen is practical, the degree of pituitary-adrenal suppression can be minimized.
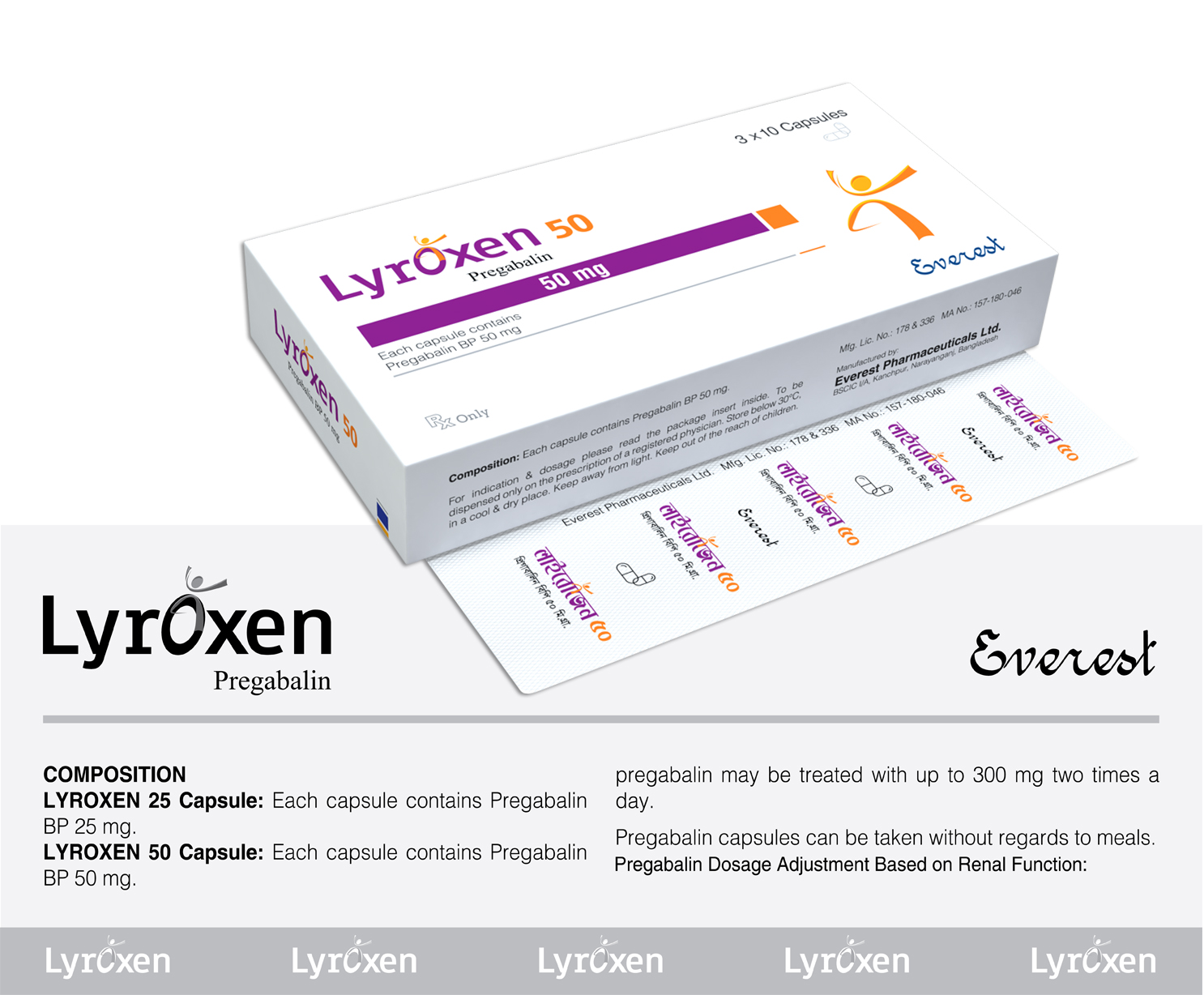
Central Nervous System
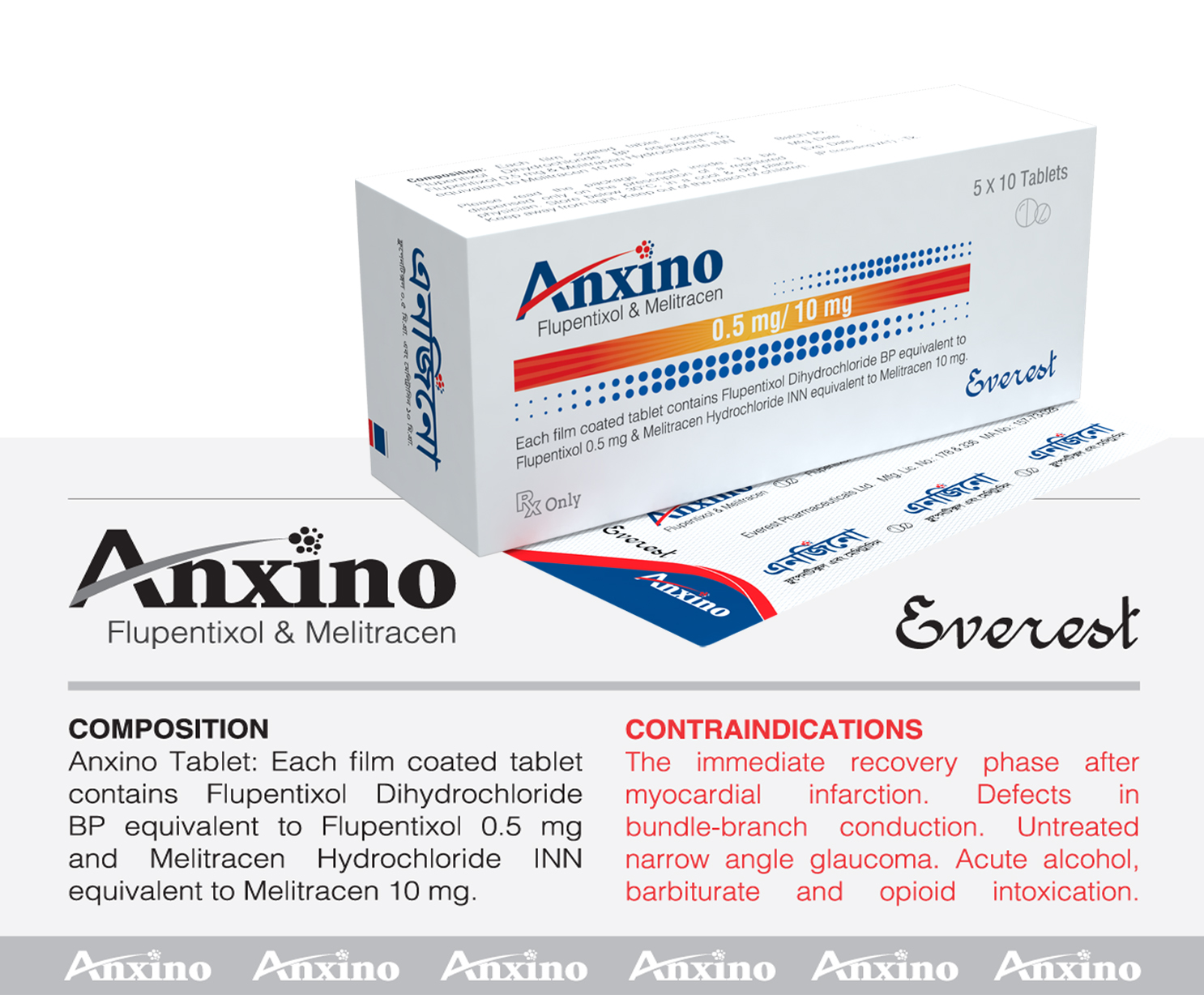
Central Nervous System

Respiratory Medicines

Central Nervous System

Gastro-Intestinal
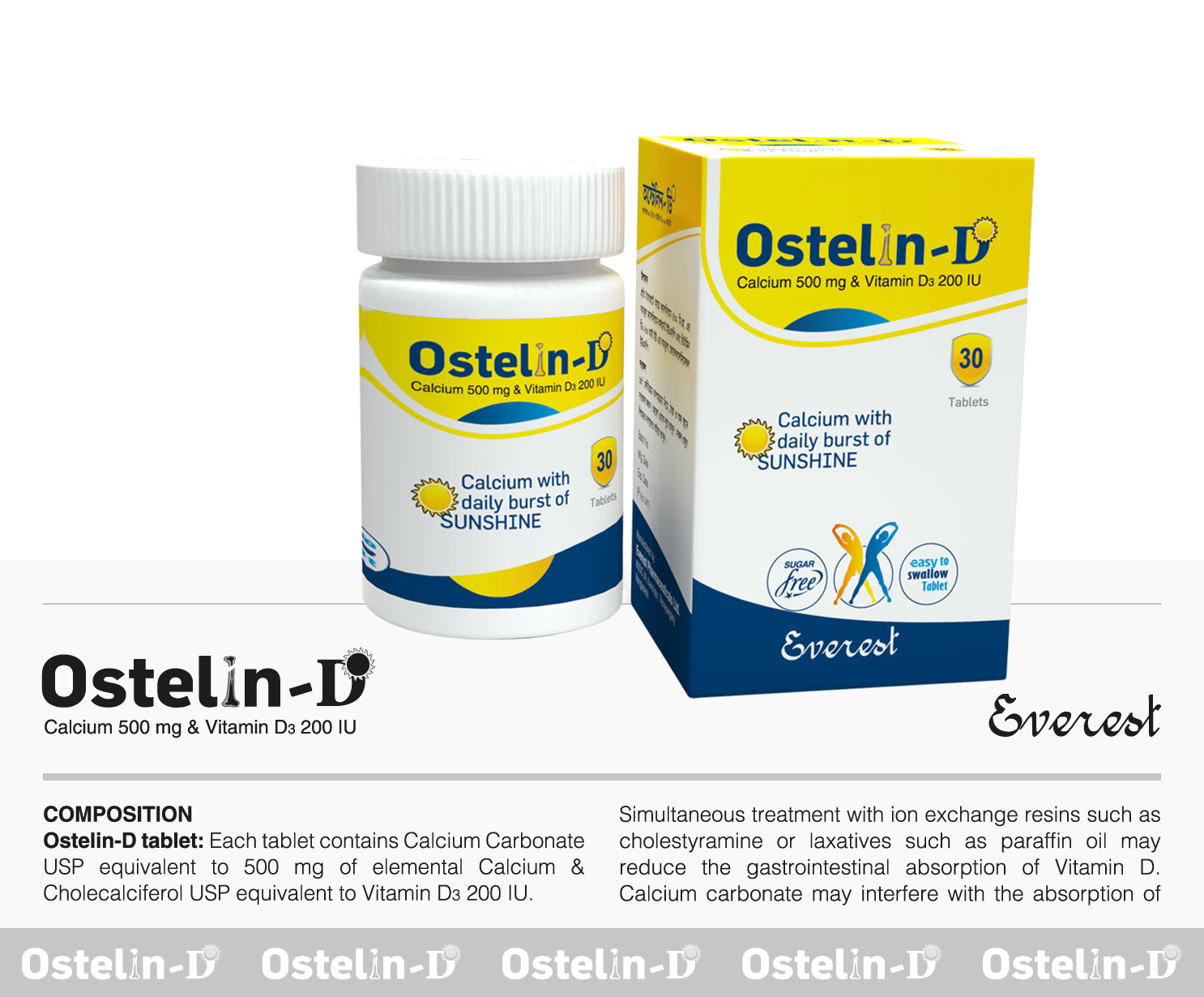
Vitamins & Minerals
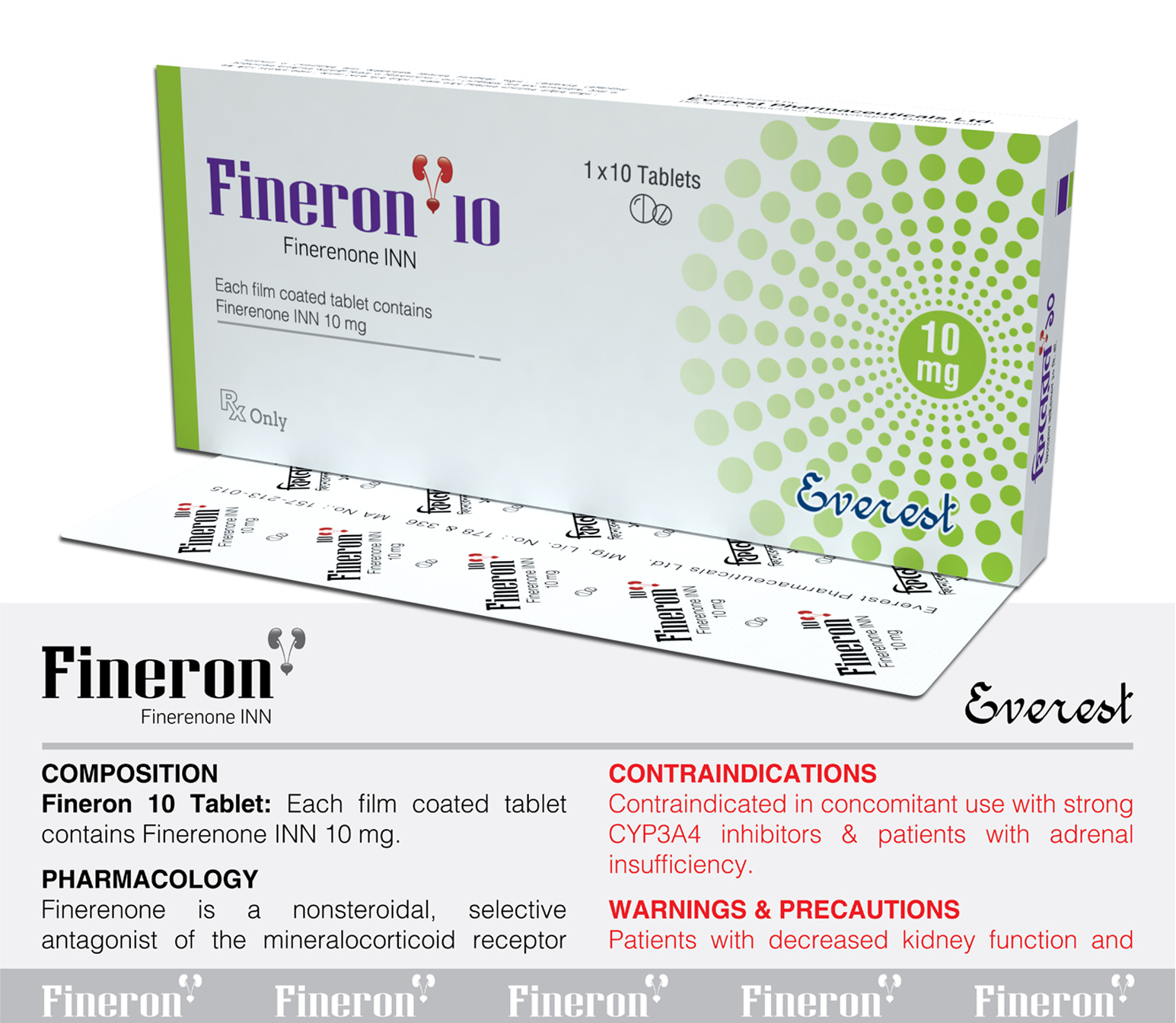
Nephrology and Urology

Anti-Fungal

Vitamins & Minerals

NSAID & Steroids